Patents
What is a patent?
A patent is an intellectual property right that protects a technical invention. It gives its holder a monopoly on the exploitation of this invention for a limited period of time, up to 20 years (and even longer if a supplementary protection certificate exists for a medicine or a phytopharmaceutical product.).
For a patent to be valid, the invention it claims must be new, involve an inventive step and be capable of industrial application.
What can be patented?
Almost anything!
Provided that it is new, inventive (not obvious) and can be used in industry. In addition, it must be something concrete (not an aesthetic creation, nor a theory, discovery or principle without practical application) and not explicitly excluded by legal provisions (offence to human dignity, public order or morality).
Examples include:
-
An object (watch, golf ball, packaging, jeans…)
-
A product (chemical, biochemical, medicine…)
-
A method or process (mechanical, chemical, electronic, biotechnological…)

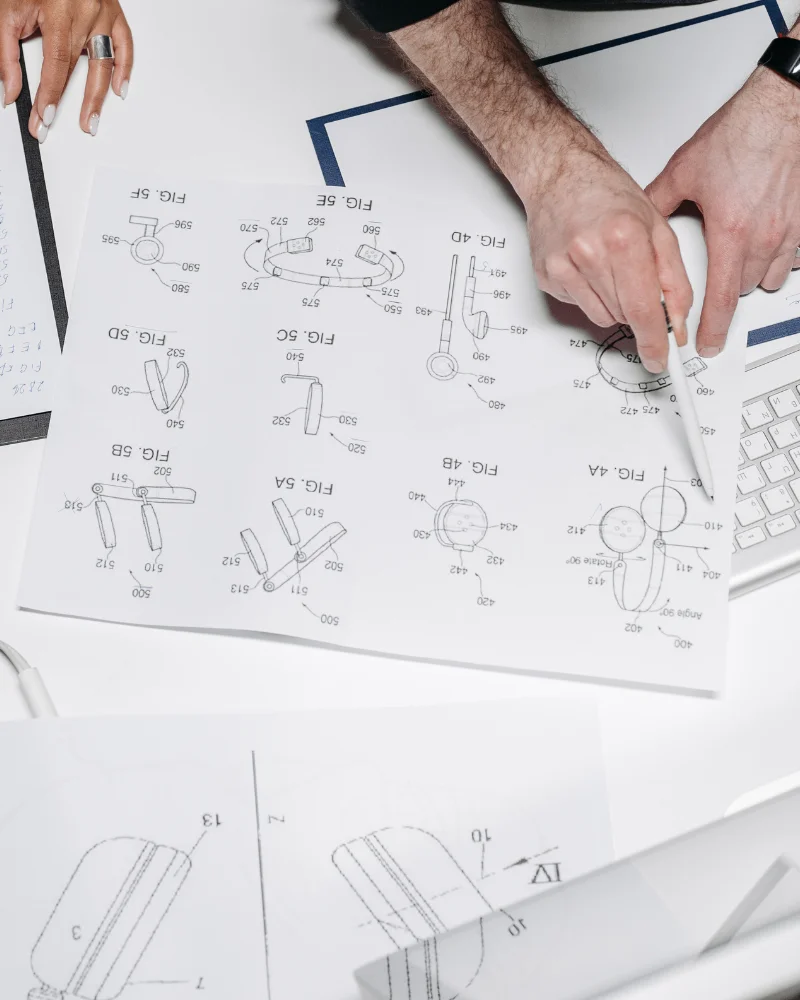
A few concrete examples:
- Alkaline Secondary Electrochemical Generators with Zinc Anode
- Silicon Powder-Based Composition for Hydrogen Production
- Sampling Method on a Coated Surface
- Easy Strap Change Wristwatch
- Variable Dial Watch
- Integrated Retractable Leash-Collar
- Respiratory Protection Mask
- Furniture Assembly Kit and Method
